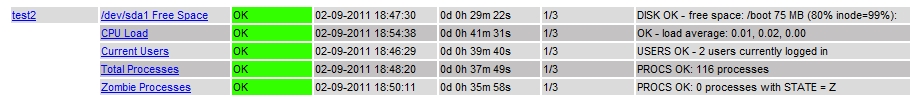
For each Linux host to monitor:
- Linux host: Install Nagios Plugins and NRPE Agent as described in NRPE documentation (say host test2)
- Linux host: Replace contents of the configuration file nrpe.cfg (default location is /usr/local/nagios/etc, remember to specify allowed_hosts parameter):
log_facility=daemon
pid_file=/var/run/nrpe.pid
server_port=5666
server_address=127.0.0.1
nrpe_user=nagios
nrpe_group=nagios
allowed_hosts=<ip-address of your Nagwin host>
dont_blame_nrpe=0
debug=0
command_timeout=60
connection_timeout=300
command=/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_users -w 5 -c 10
command=/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_load -w 15,10,5 -c 30,25,20
command=/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_disk -w 20% -c 10% -p /dev/sda1
command=/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_procs -w 5 -c 10 -s Z
command=/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_procs -w 150 -c 200 |
- Linux host: Make sure that the Nrpe service is configured properly and firewall is open for connections on port 5666.
- Nagwin host: Create the file test2.cfg in etc/nagios/nagwin directory with the following content:
# Define a host for the local machine
define host{
use linux-server
host_name test2
alias Test Linux
address ip.ad.dre.ss
}
define service{
use generic-service
host_name test2
service_description CPU Load
check_command check_nrpe!check_load
}
define service{
use generic-service
host_name test2
service_description Current Users
check_command check_nrpe!check_users
}
define service{
use generic-service
host_name test2
service_description /dev/sda1 Free Space
check_command check_nrpe!check_sda1
}
define service{
use generic-service
host_name test2
service_description Total Processes
check_command check_nrpe!check_total_procs
}
define service{
use generic-service
host_name test2
service_description Zombie Processes
check_command check_nrpe!check_zombie_procs
}
|
- Restart Nagwin_Nagios service and check results via web interface.
